Optipedia • SPIE Press books opened for your reference.
Interferograms
Excerpt from Field Guide to Interferometric Optical Testing
Spherical Aberration Interferograms
The following figures are example interferograms with their corresponding wavefront aberration and Zernike coefficients in waves.
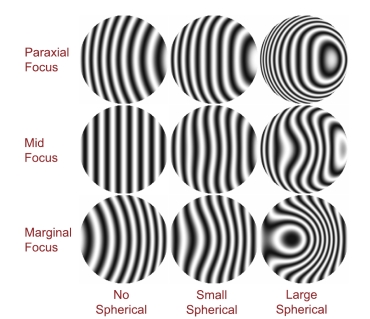
| W020=1 W040=0 Z3=1/2 Z8=0 | W020=0 W040=1 Z3=1/2 Z8=1/6 | W020=0 W040=4 Z3=2 Z8=2/3 |
| W020=0 W040=0 Z3=0 Z8=0 | W020=-1 W040=1 Z3=0 Z8=1/6 | W020=-4 W040=4 Z3=0 Z8=2/3 |
| W020=-1 W040=0 Z3=-1/2 Z8=0 | W020=-2 W040=1 Z3=-1/2 Z8=1/6 | W020=-8 W040=4 Z3=-2 Z8=2/3 |
W111=−4 and Z1=−4 for all of these interferograms.
Astigmatism Interferograms
 θ=Tilt orientation
θ=Tilt orientation
Wavefront Coefficients
W020=0
W111=4 at θ
W222=−1 at 90°
| Z0=−1/4 | Z3=−1/4 |
| Z1=4 cosθ | Z4=1/2 |
| Z2=4sinθ |

Wavefront Coefficients
W020=0
W111=1 at θ
W222=−4 at 90°
| Z0=−1 | Z3=−1 |
| Z1= cosθ | Z4=2 |
| Z2=sinθ | Z5=0 |

Wavefront Coefficients
W020=2
W111=1 at θ
W222=−4 at 90°
| Z0=0 | Z3=0 |
| Z1= cosθ | Z4=2 |
| Z2=sinθ | Z5=0 |
Citation:
View SPIE terms of use.
E. P. Goodwin and J. C. Wyant, Field Guide to Interferometric Optical Testing, SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA (2006).
View SPIE terms of use.
Excerpt from
Member:
$35.70
Non-Member: $42.00
Non-Member: $42.00

